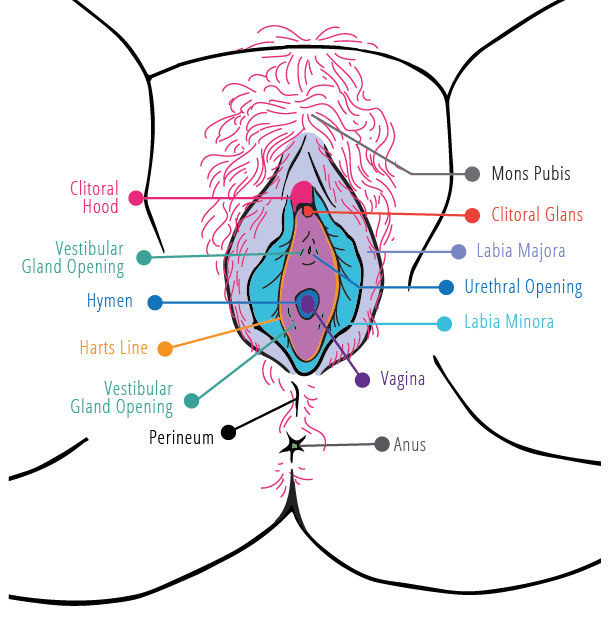
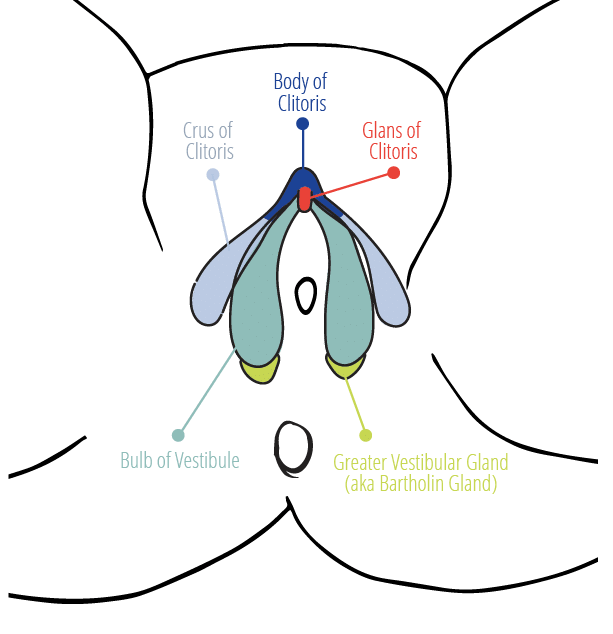
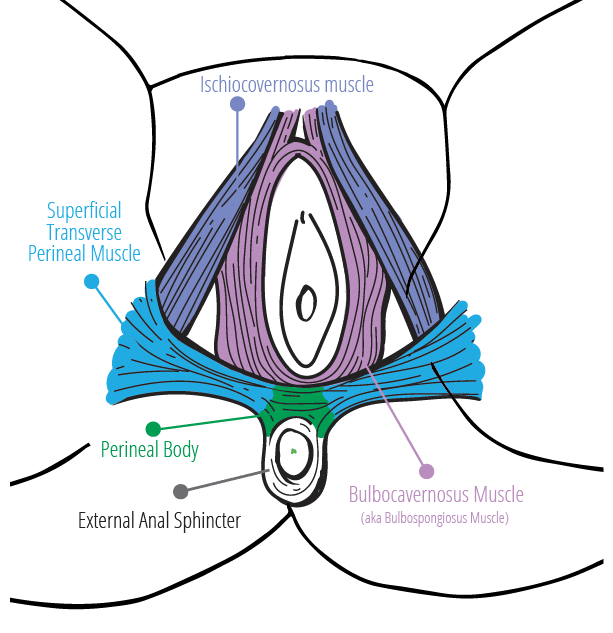
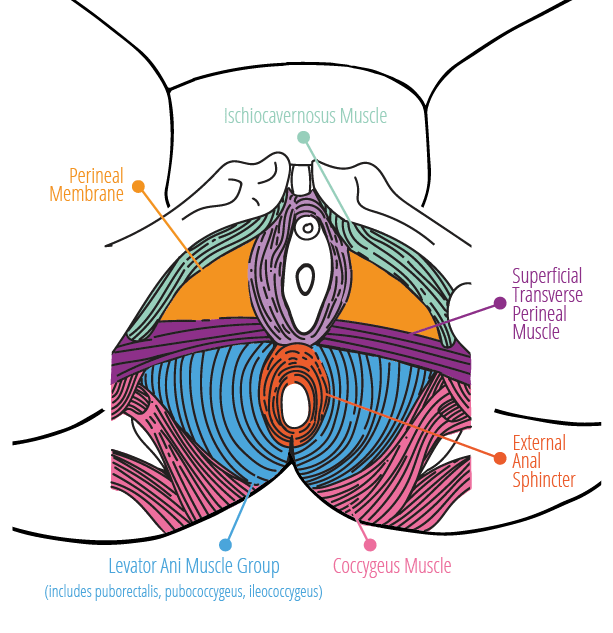
The Vulva
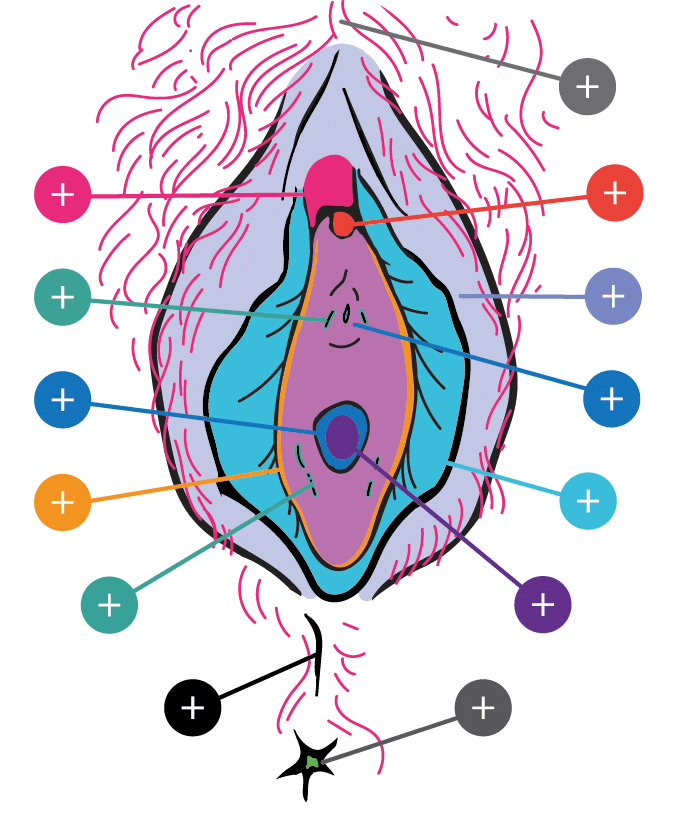
Clitoral Glans
A very sensitive organ at the top of your vulva, key for sexual pleasure.
Clitoral Hood
A small fold of skin protecting the head of your clitoris.
Hart's Line
The line where the smooth vestibule skin meets the more textured skin of your outer labia.
Labia Majora
The outer, fleshy lips of your vulva that protect the inner parts.
Labia Minora
The smaller, inner lips of the vulva that protect your vaginal opening and clitoris.
Vestibular Gland Opening
Glands near your vaginal opening that produce fluid for comfort and lubrication.
Vestibular Gland Opening
Small glands near your urethra that make lubricating fluids.
Vagina
The muscular canal that connects your vulva to your cervix and uterus.
Hymen
A thin piece of skin partially covering your vaginal opening.
Urethral Opening
The tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside of the body.
Mons Pubis
The squashy area of flesh above your labia (or lips) covered by pubic hair.